Advanced Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3): Enabling High-Tech Applications with Precision and Reliability
Abstract
Aluminum oxide(Al2O3), commonly known as alumina, is a versatile and high-performance ceramic material widely utilized across numerous advanced industries due to its exceptional dielectric strength, thermal stability, chemical inertness, and mechanical hardness. This paper outlines the key properties, applications, and technical specifications of high-purity alumina, with a focus on its critical role in semiconductor packaging and lithium-ion battery coatings. Additionally, it highlights the manufacturing and supply capabilities of UrbanMines Tech., a leading Chinese producer committed to quality, customization, and reliable export services.
1. Introduction
Alumina is not merely a raw material for aluminum production; it is a cornerstone of modern high-technology manufacturing. From microelectronics and energy storage to optics, catalysis, and protective coatings, alumina’s unique combination of properties makes it indispensable. With the growing demand for miniaturization, energy efficiency, and high reliability in electronic and energy systems, the need for precisely engineered high-purity alumina has never been greater.
2. Material Properties and Specifications
High-purity alumina is categorized by its phase, purity level, particle size distribution, and trace impurity content, each parameter tailored to specific application requirements.
2.1 Purity and Impurity Control
- High-Purity Grades: 4N (99.99%), 5N (99.999%), and 6N (99.9999%) alumina are essential for sensitive applications such as semiconductor encapsulation and optical components.
- Low Alpha-Ray Emission: Critical for semiconductor packaging to prevent soft errors in memory devices. Specifications often require Uranium (U) and Thorium (Th) content below 3 ppb, with minimal Fe, Na, and Cl impurities.
- Example Specification:
- Al₂O₃ content: ≥ 99.7%
- SiO₂: < 0.15%, Fe₂O₃: < 0.1%, Na₂O: < 0.1%
- Moisture: < 0.1%, Loss on ignition: < 0.1%
2.2 Particle Size and Morphology
Applications dictate precise granulometry:
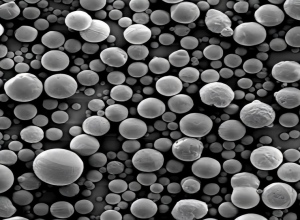
- Spherical Alumina: D50 sizes ranging from 1 µm to 45 µm (e.g., 2.8 µm, 5.8 µm for optimized packing density in semiconductors).
- Non-Spherical Alumina: D50 from 1.5–10.5 µm, used in coatings and composites where specific surface area and green density are crucial.
- BET Surface Area: Typically < 1.5 m²/g for coatings to ensure proper slurry formulation and adhesion.
2.3 Phase and Crystalline Structure
Alpha-phase alumina (α-Al2O3) is the most thermodynamically stable form, offering superior hardness, thermal conductivity, and electrical insulation. Crystal sizes of 2–3 µm are often specified for consistent sintering behavior and final microstructure.
3. Key Applications in High-Tech Industries
3.1 Semiconductor Packaging
Low-alpha spherical alumina is used as a filler in epoxy molding compounds (EMCs) to enhance thermal conductivity, reduce coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), and provide radiation shielding. Particle size distribution (e.g., bimodal 2.8 µm and 5.8 µm) is optimized for maximum packing and minimal viscosity.
3.2 Lithium-Ion Battery Separator Coatings
High-purity α-alumina (D50 < 4 µm) is applied as a ceramic coating on polymer separators. It improves thermal stability, prevents dendrite penetration, and enhances electrolyte wettability, thereby increasing battery safety and cycle life. The material is mixed with binders to form a stable slurry for uniform coating.
3.3 Other Advanced Uses
- Capacitors: As a dielectric barrier due to its wide band gap.
- Catalysis & Adsorption: High-surface-area alumina as catalyst support or desiccant.
- Structural Ceramics: In wear-resistant coatings, biomedical implants (e.g., hip replacements), and armor systems.
- Polishing & Abrasives: Ultrafine alumina (Diamantine) for precision polishing in optics and watchmaking.
- High-Temperature Insulation: As refractory linings in furnaces.
4. UrbanMines Tech.: A Reliable Partner from China
As global demand for specialty alumina grows, UrbanMines Tech. stands out as a trusted supplier with deep technical expertise and a customer-focused approach.
4.1 Manufacturing Excellence
- Our dedicated production lines in inland China are equipped to produce high-purity, low-alpha alumina with strict quality control.
- We offer flexible batch sizes—from R&D samples to full-scale production—ensuring short lead times and just-in-time supply.
4.2 Customization Capability
- We tailor purity, particle size distribution, morphology (spherical/non-spherical), and impurity profiles to meet exact customer requirements.
- Technical support is provided to assist with material selection and integration.
4.3 Proven Reliability and Export Expertise
- With 16 years of industry experience, we have built long-term relationships; over 60% of our clients have been partners for more than 5 years.
- We hold all necessary export licenses, including those for rare earth-related products, ensuring smooth and compliant international logistics.
4.4 The Advantage of “Made in China”
- China’s mature industrial ecosystem offers competitive advantages in raw material sourcing, advanced processing technologies, and scalable production.
- UrbanMines Tech. leverages these strengths while adhering to international quality standards (ISO, RoHS, REACH).
5. Conclusion
High-purity aluminum oxide is a critical enabler of innovation in electronics, energy storage, and advanced ceramics. Meeting the stringent requirements of modern applications demands not only advanced material science but also a reliable and agile supply chain. UrbanMines Tech. combines high-performance product offerings with responsive customization and dependable export services, making it an ideal partner for global clients seeking quality alumina solutions.